Video: Maren Hadley talks about pre-reading measures.
Few studies have been conducted regarding the validity and reliability of pre-reading progress monitoring procedures that can be used with students who are deaf or hard of hearing. Three procedures have been used in small studies with students who are deaf, hard of hearing or are cochlear implant users (3). These include: Picture Naming, Letter Identification and Isolated Words.
Picture Naming is a process used to monitor students’ readiness for reading. Picture naming is a criterion-referenced procedure that may be used to monitor a student’s growth in the development of language, a prerequisite for reading and written expression. Picture naming is administered individually and can be given as a weekly measure or more frequently.
Procedure:
The child is presented with pictures of objects commonly found in preschoolers’ natural environments (i.e., home, classroom, community), one at a time. The child is told to name the pictures as quickly as possible. Each picture naming task may be given in either 30 sec. or 1 minute sets; the length depends on the language skills and attention of the child.
Categories of objects used in the picture naming task include animals, food, people, household objects, vehicles, tools, and clothing.
After providing a set of sample items, the teacher or teacher’s assistant directs the child to look at each card and name it as quickly as possible. If the child does not respond within 4 seconds, the response is incorrect and a new picture is displayed. After exactly one minute (or 30 seconds) the activity stops. The total number of pictures named correctly within a 1 minute or 30 second time period is the score. Responses may be spoken or signed.

Letter Naming is used with kindergarten or older beginning readers. It is a procedure when conducted orally or using Cued Speech symbols, may be used to indicate the student’s ability to associate a phoneme with the graphic equivalent. Letter naming (using fingerspelling) is an indicator of the student’s ability to associate the correctly fingerspelled letter with its graphic representation.
Procedure:
The child is presented with a letter (capital and lower case) printed on individual cards one at a time. The child is told to name the letter as quickly as possible. Each letter naming task is 1 minute. If a child does not respond within 4 seconds, the item is incorrect.
The score generated is the number of correctly fingerspelled letters in 1 minute.
There is no research that indicates letter naming or phonemic awareness among students who are deaf or hard of hearing is a predictor of subsequent reading ability.
Rhyming is generally not used with students who are deaf or hard of hearing as a predictor of reading or prerequisite for reading. However, the rhyming process appears to be a useful measure to monitor student progress in developing auditory discrimination and comprehension skills. This process may be particularly useful for teachers providing compensatory skills to children with cochlear implants and hearing aids.

Procedure:
The teacher or teacher’s assistant presents a child with stimulus cards that include a target photo or line drawing at the top of each card (e.g., bees) and a set of three photos/drawings in a row at the bottom of each card (e.g., pants, gate, cheese), one of which rhymes with the target picture.
After providing a set of sample items, the teacher directs the child to look at each card and point to one of the three pictures at the bottom of the card that sounds the same as (or rhymes with) the target picture. If the child does not respond within 4 seconds, the item is incorrect and the next card is displayed.
This is a 2- minute task. The score is the number of correct rhyming pictures identified within two minutes.
There is no research that indicates the association between rhyming and reading among students who are deaf or hard of hearing is a predictor of subsequent reading ability.
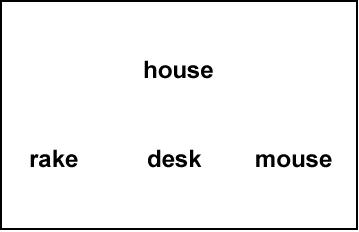
Alliteration is a task that requires the child to identify an illustration that begins with the same sound or phoneme as a target word. Alliteration is generally not used with students who are deaf or hard of hearing as a predictor of reading competencies or prerequisite for reading. However, the alliteration process may be a useful measure to monitor student progress in developing auditory discrimination and comprehension skills. This process may be useful for teachers providing compensatory skills to children with cochlear implants and hearing aids.


Procedure:
The teacher or teacher’s assistant presents a child with stimulus cards that include a picture at the top of each card (e.g., rain) and a set of three images in a row at the bottom of each card (e.g., house, rake, pig), one of which starts with the same sound as the target picture. After providing a set of sample items, the examiner asks the child to look at each card and point to one of the three pictures at the bottom of the card with the same initial sound as the target picture. The task continues for a total of two minutes. The score is the number of pictures the child correctly identifies within two minutes.
Isolated Words is a process used to monitor students’ readiness for reading. Naming isolated words is a criterion-referenced procedure that may be used to monitor a student’s growth in the development of language and readiness for reading narrative text. The words used in the task may be taken from the Dolch word list or the Most Frequently Used Words in the English Language (4). Isolated word reading is administered individually and can be given as a weekly measure or more frequently.
Procedure:
The child is presented with isolated words printed on cards. Each card is presented to the child. The child is told to say or sign the word as quickly as possible.
After demonstrating the task with the student, the teacher or teacher’s aide directs the student to look at each card and say it or sign it as quickly as possible. If the child does not respond within 4 seconds, the response is incorrect.
After one minute the activity stops. The total number of correct words is the score.
